Which nutrient helps alleviate the pain of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis,[1] supports brain and skin health and also reduces the risk of chronic diseases including cardiovascular disease?[2] Not sure? Here’s a hint: it’s found in seafood and is particularly abundant in fish.
If you answered omega-3, you are correct! This essential nutrient provides a wide variety of health benefits as it is required for the healthy functioning of almost every cell in your body. Omega-3 cannot be produced by the body and must be consumed from the diet or through supplementation. Alarmingly, only 20% of adults meet the recommended daily intake (RDI) of this vital nutrient, with only 10% able to do so without taking a supplement.[3] It is for this reason, a good quality fish oil is recommended to ensure adequate intake of omega-3.
Alarmingly, only 20% of adults meet the recommended daily intake (RDI) of this vital nutrient, with only 10% able to do so without taking a supplement.
What fish oil can do for you
Omega-3 is important for all ages and stages of life, from unborn babies to the elderly. During pregnancy, omega-3 plays a pivotal role in foetal development[4] and also reduces the risk of premature birth.[5] It supports healthy brain and nervous system development throughout childhood,[6] and also benefits adult brains by reducing the risk of mood disorders such as depression.[7] In later adulthood, omega-3 reduces mild cognitive and memory impairment[8] and may assist in the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease.[9] It also reduces the risk of some major chronic diseases prevalent in Western society, such as cardiovascular disease and heart attack.[10] Additionally, it is beneficial for conditions characterised by pain and inflammation, such as arthritis.[11] Due to its diverse health benefits, it is important you choose a high-quality fish oil to ensure you get the most out of your supplementation.
Quality fish oil for best results
When looking for a fish oil supplement, you may be tempted to buy bulk quantities at a cheaper price. However, in the case of fish oil, you get what you pay for. Fish oil supplements that have not been sourced from a quality supplier or undergone rigorous quality testing often contain higher amounts of contaminants such as heavy metals and pesticides, and/or higher levels of oxidation (rancidity). Oxidation causes an unpleasant fishy odour and taste, reduces fish oil’s effectiveness[12] and may even be harmful to your health. In the case of fish oil, you get what you pay for.
When looking for a fish oil supplement, you may be tempted to buy bulk quantities at a cheaper price. However, in the case of fish oil, you get what you pay for.
To get the full benefits of omega-3, I recommend choosing a high quality fish oil that meets the following criteria:
- Sustainable: Look for products that are certified by Friends of the Sea so you know the fish are sourced via sustainable and eco-friendly fishing practices.
- Clean: Choose a fish oil that is made from small, cold water, pelagic fish. These fish occupy positions lower in the marine food chain and therefore accumulate fewer contaminants such as heavy metals and pesticides. Also, look for products that are further purified by molecular distillation to remove any remaining contaminants.
- Concentrated: Dosage is critical to the results you experience, with a recent review finding fish oil to be ineffective at lower doses.[13] Ensure you chose a fish oil supplement that provides a therapeutic dose of EPA and DHA containing at least 500 mg and 200 mg per capsule, respectively.
- Fresh: The fish oil you choose should be manufactured using processes that minimise exposure to environmental factors such as air, heat and light to minimise oxidation. For added protection, look for fish oils that are twice-nitrogen flushed – a process where nitrogen is used to remove oxygen within the bottle to reduce oxidation over time.
- Tested: Fish oil should be tested at all stages of manufacture to ensure the final product is free from contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals and oxidation.

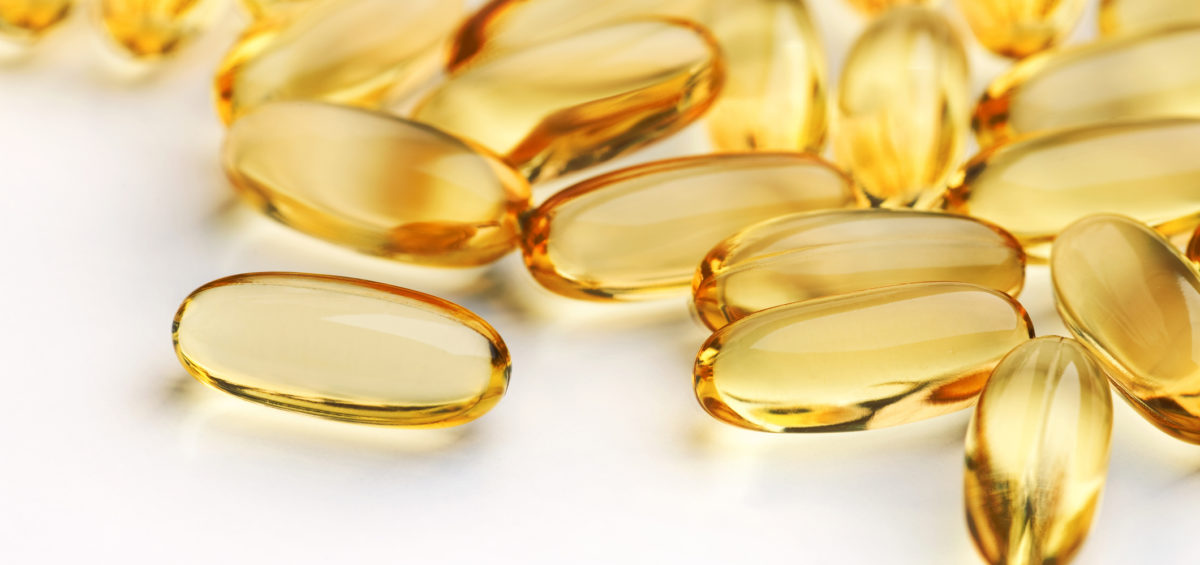
If this sounds a little too complicated, don’t worry, the easiest way to access a high-quality fish oil is to see a Natural Healthcare Practitioner, who can prescribe a Practitioner-only fish oil that meets all of the above criteria. Additionally, a Practitioner will be able to assess your health and omega-3 needs (via Omega-3 Testing or dietary assessment), allowing them to recommend the specific dose necessary for you.
Talk to a Natural Healthcare Practitioner today to find the right fish oil supplement for you.
[1] Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients. 2010 Mar;2(3):355-74. doi: 10.3390/nu2030355.
[2] Harris WS, Tintle NL, Etherton MR, Vasan RS. Erythrocyte long-chain omega-3 fatty acid levels are inversely associated with mortality and with incident cardiovascular disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Journal Clin Lipidol. 2018 May 1;12(3):718-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2018.02.010.
[3] Meyer B. Australians are not meeting the recommended intakes for omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids: results of an analysis from the 2011–2012 national nutrition and physical activity survey. Nutrients. 2016 Mar;8(3):111. doi: 10.3390/nu8030111.
[4] Kawakita E, Hashimoto M, Shido O. Docosahexaenoic acid promotes neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience. 2006;139(3):991-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.021.
[5] Middleton P, Gomersall JC, Gould JF, Shepherd E, Olsen SF, Makrides M. Omega‐3 fatty acid addition during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018(11). doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003402.pub3.
[6] Kawakita E, Hashimoto M, Shido O. Docosahexaenoic acid promotes neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience. 2006;139(3):991-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.021.
[7] Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Yassini-Ardakani M, Karamati M, Shariati-Bafghi SE. Eicosapentaenoic acid versus docosahexaenoic acid in mild-to-moderate depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;23:636–644. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.08.003.
[8] Yurko-Mauro K, Alexander D, Van Elswyk M. Docosahexaenoic acid and adult memory: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):1-18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120391.
[9] La Rosa F, Clerici M, Ratto D, Occhinegro A, Licito A, Romeo M, et al. The gut-brain axis in Alzheimer’s Disease and omega-3: a critical overview of clinical trials. Nutrients. 2018 Sep 8;10(9):1267. doi: 10.3390/nu10091267.
[10] Harris WS, Tintle NL, Etherton MR, Vasan RS. Erythrocyte long-chain omega-3 fatty acid levels are inversely associated with mortality and with incident cardiovascular disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Journal Clin Lipidol. 2018 May 1;12(3):718-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2018.02.010.
[11] Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients. 2010 Mar;2(3):355-74. doi: 10.3390/nu2030355.
[xii] Rundblad A, Holven KB, Ottestad I, Myhrstad MC, Ulven SM. High-quality fish oil has a more favourable effect than oxidised fish oil on intermediate-density lipoprotein and LDL subclasses: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2017 May;117(9):1291-8. doi: 10.1155/2013/464921.
[xiii] Abdelhamid AS, Brown TJ, Brainard JS, Biswas P, Thorpe GC, Moore HJ et al. Omega‐3 fatty acids for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018(11). doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003177.pub3.








Leave a Comment